Chapter 8 Real Gases. - ppt download
4.5 (446) In stock
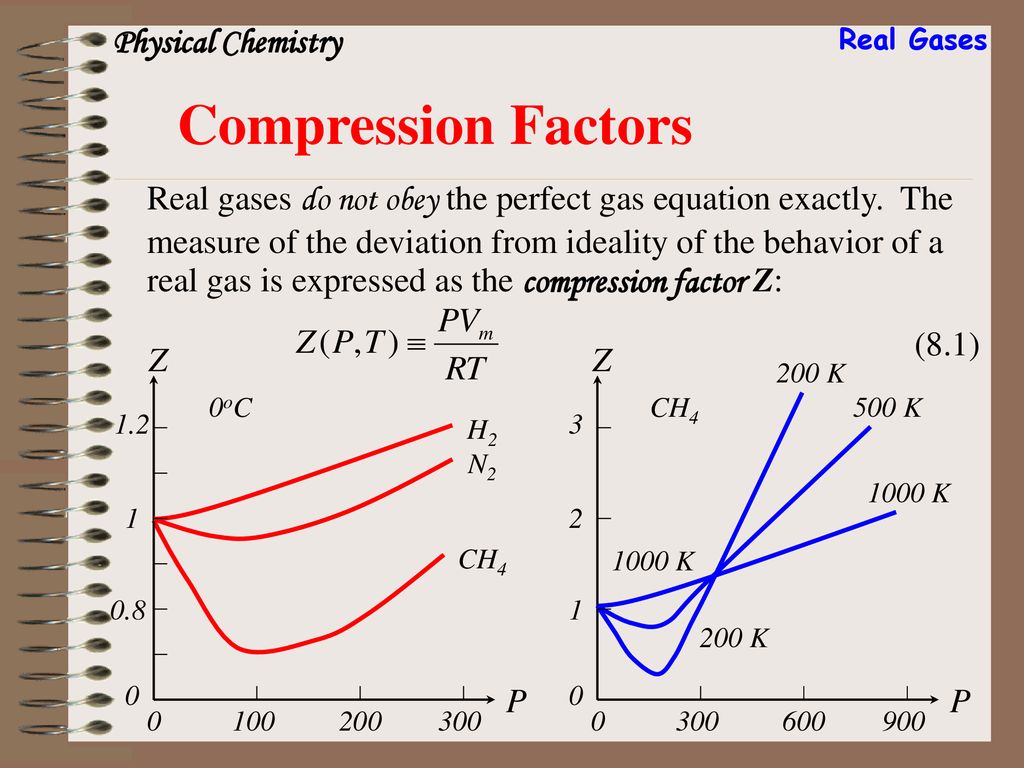
Compression Factors Physical Chemistry Real Gases Compression Factors Real gases do not obey the perfect gas equation exactly. The measure of the deviation from ideality of the behavior of a real gas is expressed as the compression factor Z: (8.1) Z P H oC N2 CH4 Z P 200 K 500 K 1000 K CH4
Real Gases. Compression Factors. Real gases do not obey the perfect gas equation exactly. The measure of the deviation from ideality of the behavior of a real gas is expressed as the compression factor Z: (8.1) Z. P. H oC. N2. CH4. Z. P. 200 K. 500 K K CH4.
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Real Gas Equations of State. (8.2) van der Waals equation. Ideal Gas Law/Perfect Gas Equation: PV = nRT (1.18)*
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Van der Waals Equation of State. : to correct the effect of intermolecular attractive forces on the gas pressure. b: the volume excluded by intermolecular repulsive forces.
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Real Gas Equations of State. Redlich-Kwong Equation. (8.3) Virial Equation of State. (8.4) The limited accuracy of the data allows evaluation of only B(T) and sometimes C(T).
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Virial Equation of State. Power series in 1/Vm. (8.4) Power series in P. (8.5) (8.6) low P. (8.7) (8.2) vdW gas.
Real Gases. Gas Mixtures. For a mixture of two gases, 1 and 2, use a two-parameter equation, (8.10) x1 and x2: the mole fractions of the components. b: a weighted average of b1 and b2. a: related to intermolecular attractions. (a1a2)1/2: intermolecular interaction between gases 1 and 2. (8.11) mean molar volume.
Real Gases. Condensation. T < 374 oC. P. H. gas condenses to liquid when P H2O. T = 300 oC. Y. G. R(vapor)S(saturated vapor), P, V U. T. S. W. M. R. 400 oC. S(saturated vapor)W(saturated liquid), P, V J. N. 374 oC. L. V. 300 oC. L. 200 oC. L + V. W(saturated liquid)Y(liquid), P , V K. Vm. Isotherms of H2O.
Real Gases. H2O phase diagram: P — T. D. C. 218 atm. Y. I. solid. liquid. S. P / 10 5 Pa. 1 atm. R. gas A. O Tf. T3. Tb. t/℃
Real Gases. Condensation. T 374 oC. Isotherms of H2O. P. Vm. U. R. J. N. Y. 374 oC. 300 oC. 200 oC. H2O. L + V. L. V. G. H. T. S. K. M. W. Fig No amount of compression will cause the separation out of a liquid phase in equil. with the gas. 400 oC. T = 374 oC. Critical temperature Tc. Critical pressure Pc. Critical volume Vm,c. Critical constants.
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Isotherms of CO2. {P} {Vm,c} T3. c. Tc. g. b. a. l. T1. T2. Critical constants. Critical T (Tc), Tc(CO2)=304.2 K. Critical P (Pc), Pc(CO2)=7.38 MPa. Critical molar V (Vm,c), Vm,c(CO2)=94×10-6 m3·mol-1.
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Table 8.1 Critical Constants. Species Tc / K Pc / atm Vm,c / cm3·mol-1. Ar Ne N H2O D2O H2S CO HCl CH3OH
Real Gases. Fluid. There is a continuity between the gaseous and the liquid states. In recognition of this continuity, the term fluid is used to mean either a liquid or a gas. An ordinary liquid can be viewed as a very dense gas. Only when both phases are present in the system is there a clear-cut distinction between liquid and gaseous states. For a single-phase liquid system it is customary to define as a liquid a fluid whose temperature is below Tc and whose molar volume is less than Vm,c. If these two conditions are not met, the liquid is called a gas. So a further distinction between gas and vapor can be made, but these two words are used interchangeably in this book.
Real Gases. Supercritical fluid. A supercritical fluid is one whose T and P satisfy. T > Tc and P > Pc. A supercritical fiquid usually has liquidlike density but its viscosity is much lower than typical for a liquid and diffusion coefficients in it are much higher than in liquids.
Real Gases. CO B ℃ t. c= t/ o. C. gas. liquid. solid p. /MPa. P. c. =7.38MPa. A MPa. Supercritical fluid. Supercritical CO2 is used commercially as a solvent to decaffeinate coffee.
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Critical data and equations of state. At the critical point: (8.12) Differentiating the van der Waals equation (8.2) and. Application of the conditions (8.12) gives. and. (8.13)
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Critical data and equations of state. From van der Waals equation: (8.14) Division of the first equation in (8.13) by the second yields. (8.15) Use of (8.15) in the first equation in (8.13) gives. and. (8.16)
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Critical data and equations of state. Substitution of (8.15) and (8.16) into (8.14) (8.15) (8.16) (8.14) gives. (8.17)
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Critical data and equations of state. Substitution of (8.15) and (8.16) into (8.14) (8.15) (8.16) (8.17) Three equations for two parameters, a and b. vdW gas. (8.18)
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Critical data and equations of state. Combination of (8.15) to (8.17) (8.15) (8.16) (8.17) Predicts the compressibility factor at the critical point. (8.19) Van der waals equation.
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Critical data and equations of state. Van der waals equation. (8.19) ideal gas. R-K equation. (8.20) (8.21) (8.22)
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Selected equations of state. Equation. Critical. constants. Perfect gas. van der Waals. Berthelot.
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. Selected equations of state. Equation. Critical. constants. Perfect gas. R-K. virial.
Physical Chemistry. Real Gases. The law of corresponding states. The critical constants are characteristic properties of gases. The reduced variables of a gas by dividing the actual variable by the corresponding constant. (8.27) reduced pressure. reduced volume. reduced temperature. The observation that the real gases at the same reduced volume and reduced temperature exert the same reduced pressure is called the law (principle) of corresponding states. (8.28)

Project Prioritization: The Ultimate Guide

Powerpoint (PPT) Templates - FREE Download
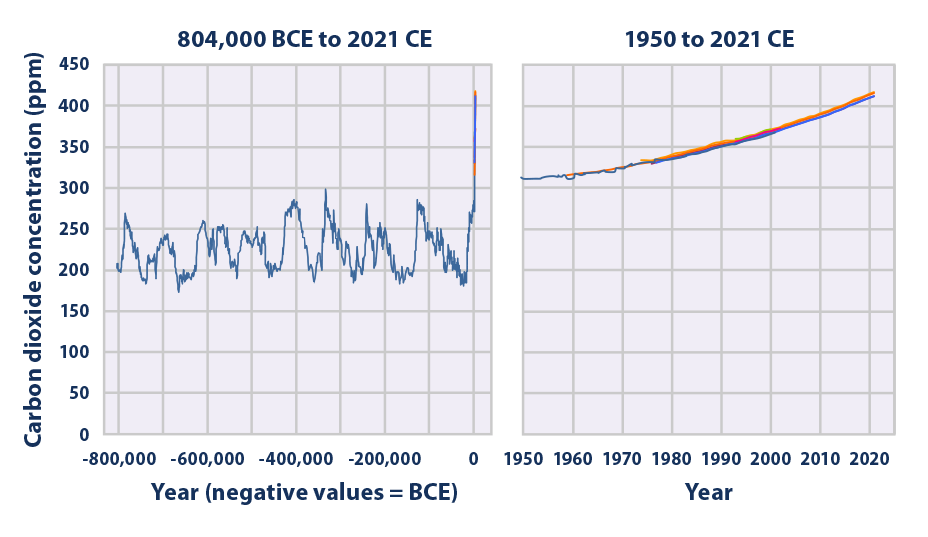
Climate Change Indicators: Atmospheric Concentrations of Greenhouse Gases
Branches of Physics (Free PDF) - Leverage Edu

Joule Thomson Effect Definition - Joule Thomson Coefficient

54 Real BCG Presentations, free to download - Slideworks

Fox Facts & Worksheets for Kids Types, Habitat, Diet, Cultural Impact

PPT - Chapter 8 Gases PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:5761357

Acids & Bases, Differences, Example & Characteristics - Lesson
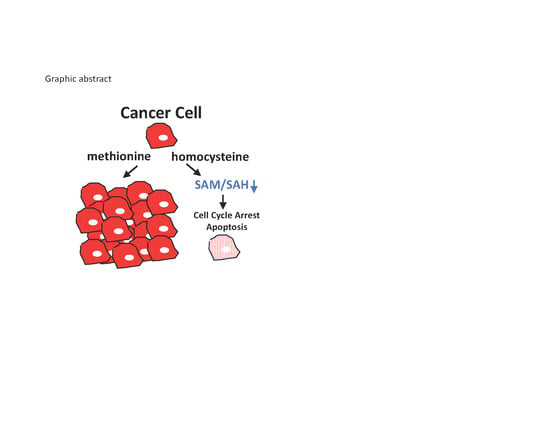
Biomolecules, Free Full-Text

Venn Diagram Ideas For PowerPoint Presentations

Element in Chemistry, Definition, Parts & Properties - Lesson

Originals: How Non-Conformists Move the World: Grant, Adam, Sandberg, Sheryl: 9780143128854: : Books

PPT - Chapter 8 Gases PowerPoint Presentation, free download - ID:662039
Solved) - For values of z near 1, it is a good approximation to write z(P) = - (1 Answer)
Solved Question 2 2.1 Consider an equation of state for a
The Compression Factor, Z, and Real Gases - What you NEED to Know
 Male Compression Full Bodysuit
Male Compression Full Bodysuit Grey cropped Lululemon leggings, fits sizes 2-6. - Depop
Grey cropped Lululemon leggings, fits sizes 2-6. - Depop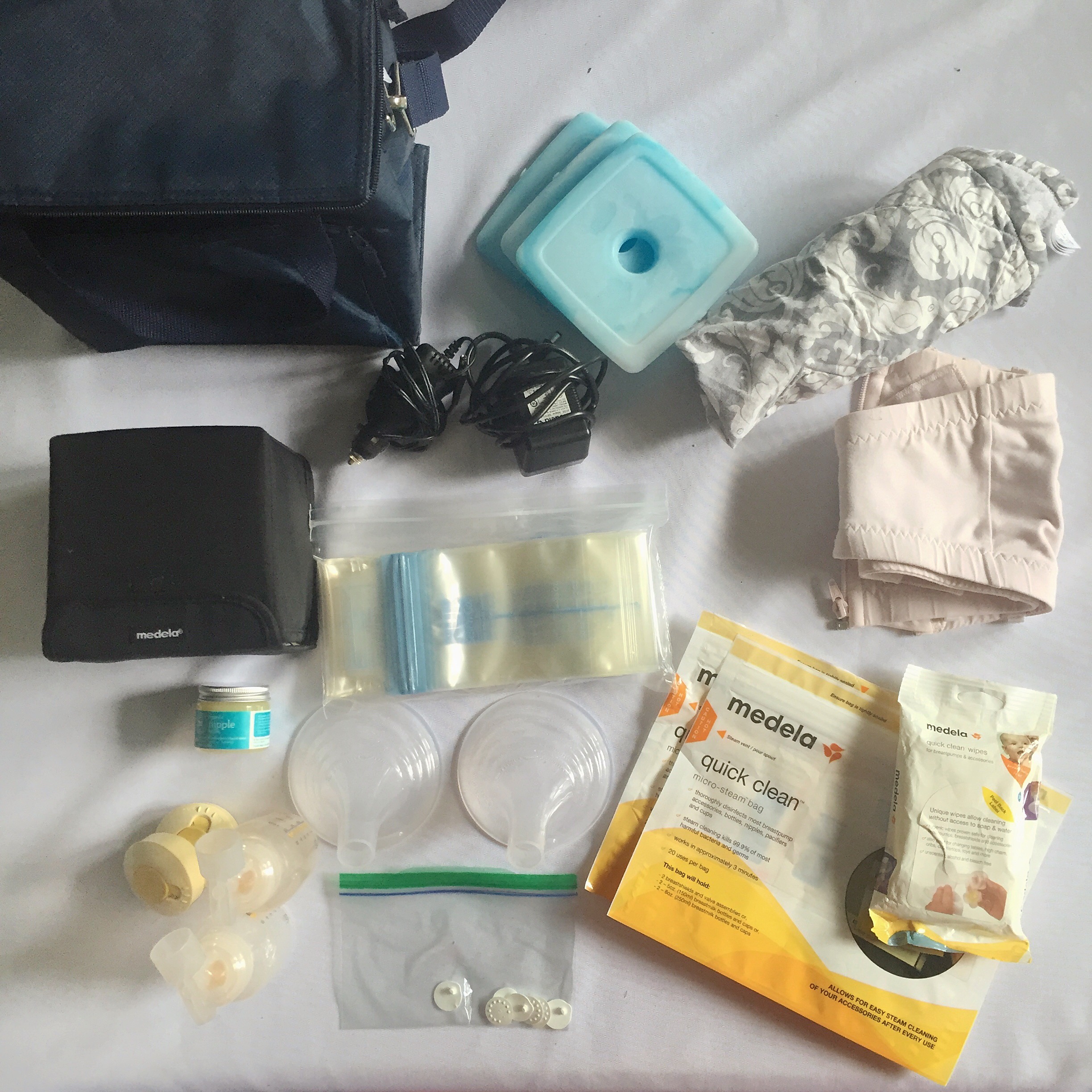 Pumping While Traveling Without a Baby — Veggies & Virtue
Pumping While Traveling Without a Baby — Veggies & Virtue Casual Shoes Tennis Shoes Sport Running Sneakers Breathable
Casual Shoes Tennis Shoes Sport Running Sneakers Breathable Lavento Women's All Day Soft Yoga Leggings 23/ 25/ 28 - No Front Seam Workout Active Legging for Women
Lavento Women's All Day Soft Yoga Leggings 23/ 25/ 28 - No Front Seam Workout Active Legging for Women Fantasie Illusion Side Support Bra Berry – Victoria's Attic
Fantasie Illusion Side Support Bra Berry – Victoria's Attic