Pathophysiology of Crohn's disease inflammation and recurrence, Biology Direct
4.8 (386) In stock
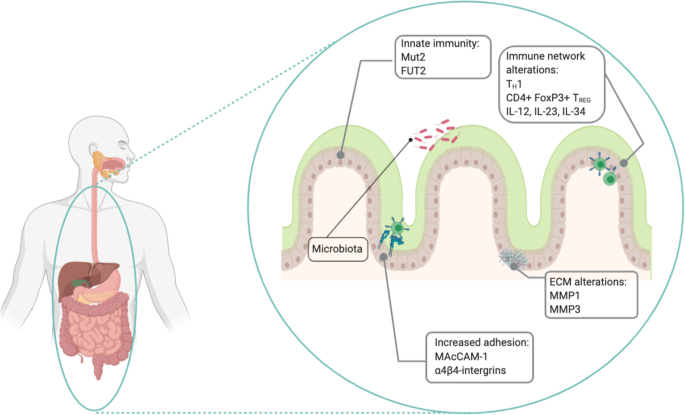
Chron’s Disease is a chronic inflammatory intestinal disease, first described at the beginning of the last century. The disease is characterized by the alternation of periods of flares and remissions influenced by a complex pathogenesis in which inflammation plays a key role. Crohn’s disease evolution is mediated by a complex alteration of the inflammatory response which is characterized by alterations of the innate immunity of the intestinal mucosa barrier together with a remodeling of the extracellular matrix through the expression of metalloproteins and increased adhesion molecules expression, such as MAcCAM-1. This reshaped microenvironment enhances leucocytes migration in the sites of inflammation, promoting a TH1 response, through the production of cytokines such as IL-12 and TNF-α. IL-12 itself and IL-23 have been targeted for the medical treatment of CD. Giving the limited success of medical therapies, the treatment of the disease is invariably surgical. This review will highlight the role of inflammation in CD and describe the surgical approaches for the prevention of the almost inevitable recurrence.

Crohn's disease - ScienceDirect

Crohn's disease - Wikipedia

Crohn's Disease Features in Anastomotic Biopsies from Patients With and Without Crohn's Disease: Diagnostic and Prognostic Value - Modern Pathology

PDF] Pathogenesis of Crohn's disease

Genetics and pathogenesis of inflammatory bowel disease

Surgical Management of Crohn's Disease: An Overview

Enfermedad de Crohn, PDF, Digestión
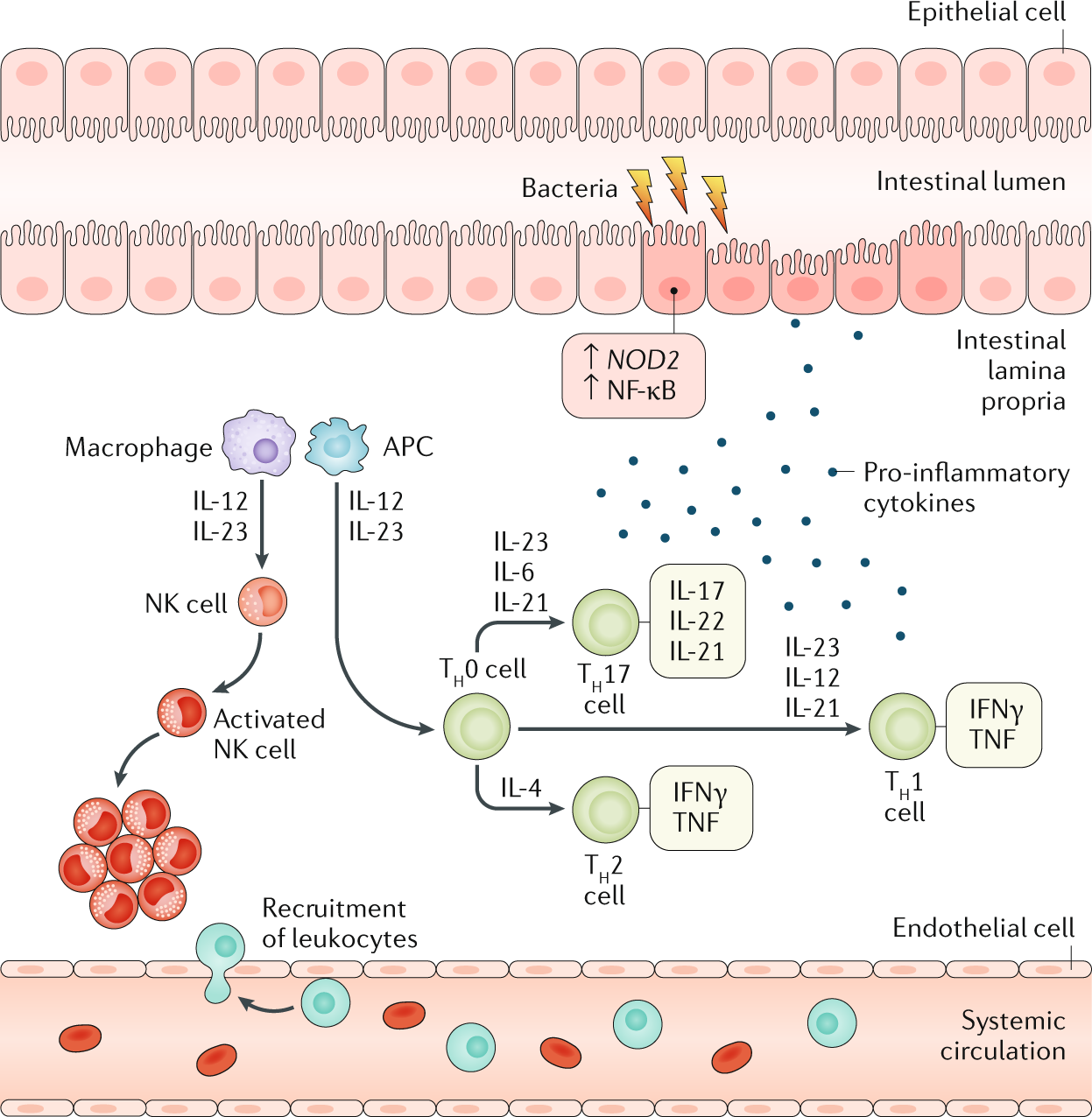
Crohn's disease Nature Reviews Disease Primers
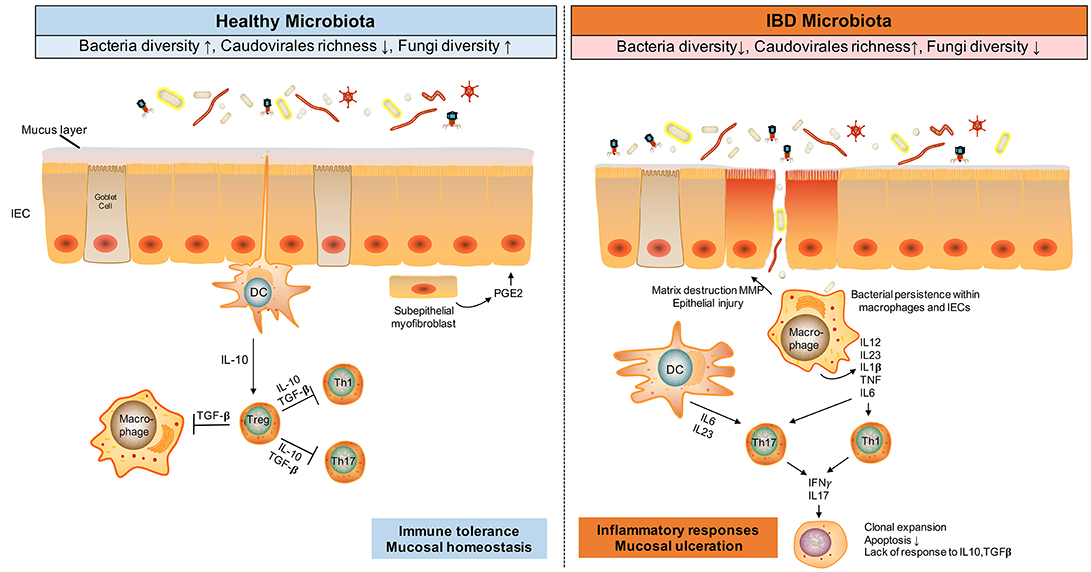
Frontiers The Gut Microbiota in the Pathogenesis and Therapeutics of Inflammatory Bowel Disease
Abdominal Surgery for Crohn's disease
Crohn's Disease Lehigh Valley Health Network
Overview of Crohn's Disease Crohn's & Colitis Foundation
Crohn's Disease Signs and Symptoms (& Why They Occur), and Complications & Deficiencies
 primadonna-couture-black-balcony-bra-side-view - Victoria's Little Bra Shop
primadonna-couture-black-balcony-bra-side-view - Victoria's Little Bra Shop:strip_icc()/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_59edd422c0c84a879bd37670ae4f538a/internal_photos/bs/2021/f/Z/dmB1sURyqssUEPZmvL6w/50860413316-34b44570b9-c.jpg) Empresa de irrigação apresenta plano de expansão em Uberaba, Triângulo Mineiro
Empresa de irrigação apresenta plano de expansão em Uberaba, Triângulo Mineiro Happens to the best of us Essential T-Shirt for Sale by LettuceChopper
Happens to the best of us Essential T-Shirt for Sale by LettuceChopper Un abdomen plano - Clínica de Cirugía Estética Madrid
Un abdomen plano - Clínica de Cirugía Estética Madrid Buy Crosshatch Mens Three Pack Mayview Joggers Black/Light Grey Marl/Navy
Buy Crosshatch Mens Three Pack Mayview Joggers Black/Light Grey Marl/Navy Brass Round Wall Mirror 30
Brass Round Wall Mirror 30